Human Leukocyte Antigen Analysis
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecules are highly polymorphic membrane proteins that play a central role in immune recognition and compatibility. In transplantation diagnostics, differences in HLA expression between donor and recipient can lead to immune rejection, making accurate HLA typing and crossmatch testing essential for successful outcomes. Advances in molecular methods such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) now enable high-resolution HLA genotyping and sensitive chimerism monitoring. These technologies allow laboratories to detect subtle genetic variations and monitor HLA chimerism or loss of heterozygosity (LOH), both of which can have critical implications for transplant success and relapse detection1,2.
In an era where virtual crossmatch and antibody profiling tools are expanding, physical crossmatch testing remains a vital and complementary tool for confirming donor-recipient compatibility3. ¤È§úóó§ã¯Ì supports these workflows with reliable cell isolation and enrichment solutions that help your laboratory perform accurate, reproducible HLA analysis with confidence.
Below, explore a curated collection of educational resources that highlight best practices, innovations, and expert insights in HLA testing, crossmatch analysis, and chimerism monitoring.
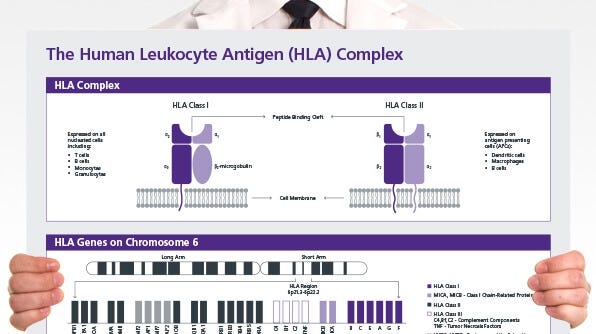
The Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Complex
This wallchart provides an overview of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex, HLA genes and nomenclature of HLA alleles.
Get Your Free Copy >Advances in HLA Typing and Genotyping
High-resolution HLA typing is essential for characterizing immune diversity and compatibility in both research and clinical applications. By integrating next-generation sequencing (NGS), laboratories can achieve detailed, allele-level insights that improve matching accuracy, uncover complex haplotypes, and enhance data interpretation. Increasingly, laboratories are adopting NGS for HLA genotyping because it delivers high-resolution results, greater accuracy through parallel sequencing, and scalable, cost-effective testing4. Supporting both clinical diagnostics and immunogenetic research, NGS-based HLA typing enables confident results for applications ranging from transplant matching to disease association studies.
Nature Research Round Table: HLA Typing Considerations for Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Banking
Learn how HLA typing and immunological compatibility influence the banking of human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC) lines for use in clinical trials. In this round table, Dr. David Turner from the Scottish National Blood Transfusion Service shares insights from his lab on donor-patient HLA matching for clinical transplants.
Physical and Virtual Crossmatch Testing
Crossmatch testing remains a key component of HLA analysis, helping assess donor-recipient compatibility before transplantation. While antibody-based and virtual crossmatch approaches have improved workflow efficiency, physical crossmatch remains a critical method to confirm reactivity and resolve ambiguous results3. Together, these complementary methods can help laboratories conduct more reliable risk assessments and informed transplantation decisions.
Cell Separation Solutions for the Flow Cytometric Crossmatch Assay
See how ñÀý¿ý¾ýã°ÏÝÞÝÒã Direct streamlines the flow cytometric crossmatch (FCXM) workflow, allowing you to isolate highly pure lymphocytes for faster, more consistent results. Learn how you can reduce assay variability and simplify sample preparation in transplant compatibility testing.
NGS-Based Chimerism Monitoring and HLA LOH Detection
After transplantation, chimerism analysis provides valuable insight into engraftment success and relapse risk. NGS-based chimerism assays offer enhanced sensitivity and the ability to detect low-level mixed chimerism that may be missed by traditional short tandem repeat (STR) methods. In parallel, HLA loss of heterozygosity (LOH) has emerged as an important molecular event, detected not only in post-transplant relapse but also in cancer and other immune-related disorders5,6. HLA LOH contributes to immune escape by enabling malignant or diseased cells to evade recognition by the host immune system7. Understanding and monitoring these genomic alterations support personalized management strategies in transplantation, oncology, and immunogenetic research.
Fully Automated, High-Purity Cell Isolation for Chimerism Labs
Discover how your lab can isolate lymphoid and myeloid lineages with >95 % purity using the automated ¡ÕÇúýºÇú°ÏÝÞÝÒã and ñÀý¿ý¾ýã°ÏÝÞÝÒã workflow, simplifying sample preparation for downstream chimerism analysis.
Supporting HLA Workflows with Cell Isolation Tools
Accurate HLA typing, crossmatch testing, and chimerism monitoring depend on high-quality cellular samples. ¤È§úóó§ã¯Ì offers reliable cell isolation and enrichment solutions, including ñÀý¿ý¾ýã°ÏÝÞÝÒãÂ, °ÏÝÞÝÒýîý¿°ìÝÞãÂ, and ¡ÕÇúý¾ÝÞ°ì°ìÝÞ°ÏÝÞÝÒãÂ, to help laboratories obtain highly pure and reproducible cell populations for downstream assays. These technologies integrate easily into existing workflows, improving consistency and efficiency in sample preparation while maintaining cell integrity for precise, reproducible results.
Cell Isolation for HLA Analysis
Equip your lab to achieve high-purity immune cell isolations (e.g. lymphoid, myeloid), so that your downstream HLA typing, crossmatch, or chimerism workflows deliver clearer, more reliable results.